A roundup of recent products in the GNSS and inertial positioning industry from the September 2023 issue of GPS World magazine.
MOBILE
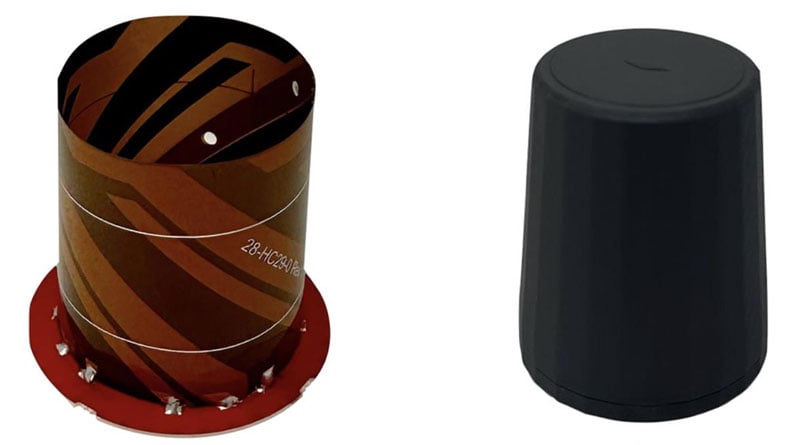
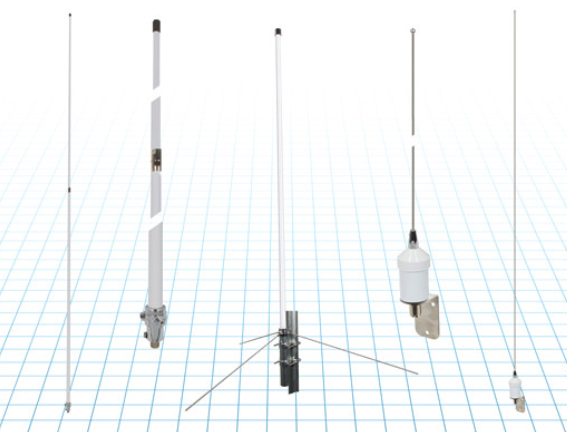
Commercial RF antennas
Marine grade for ships/boats
The Fairview commercial RF antennas provide accurate positioning with L1 band and multiband capabilities and offer a 28 dBi gain for reliable positioning. The antennas offer full-spectrum connectivity and operate within the universal marine frequency range of 156 MHz to 163 MHz and CB-27 MHz, 10m-HAM, ensuring unbroken connections at sea. The antennas are also weatherproof, rated IP67 for water ingress. They are offered with three types of mounts, making it easier to integrate into any vessel. All antennas are crafted from robust stainless steel or fiberglass for durability and reliable performance. Various antenna lengths are available for users to select based on their signal performance needs..
Fairview Microwave, fairviewmicrowave.com
SURVEYING & MAPPING
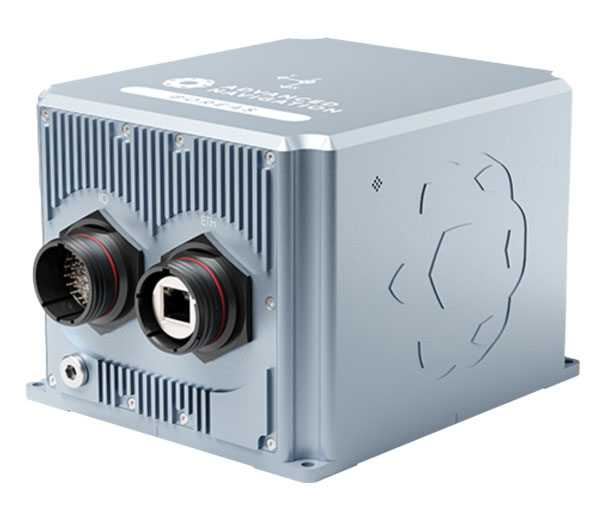
Inertial Measurement Units
Features ultra-high accuracy DFOG range and more
The Boreas A90 and A70 are strategic-grade inertial measurement units (IMU) that deliver acceleration and orientation with accuracy, stability and reliability under all conditions with no reliance on GNSS. They also feature automatic gyrocompassing. The IMUs contain ultra-high accuracy digital fiber-optic gyroscope (DFOG) range and high performance closed-loop accelerometers. The Boreas A90 and A70 are both suitable for surveying, mapping and navigation across subsea, marine, land and air applications. The Boreas A90 and A70 also offer an optional license to add inertial navigation system capabilities and enable integration with external GNSS receivers using Advanced Navigation’s range of interfaces and communication protocols.
Advanced Navigation, advancednavigation.com
GNSS Receiver
Suitable for surveying, mapping, and geographic information system applications
The Mars Laser RTK features a datalink modem that transmits and receives across the full frequency range from 410 MHz to 470 MHz. With adjustable transmit power of 0.5 w to 2 w and a maximum distance of 15 km, it meets the measurement demands of complex environments. It can also switch roles between a rover and a base, enabling more flexibility in demanding applications. The Mars Laser RTK is equipped with a Wi-Fi/4G modem and Bluetooth capabilities, facilitating reliable communication across various platforms. The Mars Laser RTK also features five LEDs on the front panel for satellite tracking, RTK corrections data and more. Powered by the SinoGNSS K8 high precision module, the device supports full-constellation and multi-frequency tracking, including GPS, GLONASS, BDS, QZSS, IRNSS, and Galileo, and supports precise-point positioning service. Additionally, the device tracks more than 60 satellites and has 1,590 channels. The Mars Laser RTK’s third-generation inertial measurement unit (IMU) supports 60° tilt with 2.5 cm accuracy. The IMU can be set to both traditional mode with range pole and to laser mode.
ComNav Technology, comnavtech.com
Desktop Solution
An Esri ArcGIS Pro add-in for field data collection software
With a streamlined user interface, the Terra Office add-in for ArcGIS Pro enables users to connect TerraFlex workflows directly to the ArcGIS platform from within ArcGIS Pro — Esri’s desktop GIS application. ArcGIS Pro users can now create and manage TerraFlex geospatial data collection projects without leaving ArcGIS. Organizations that collect data in TerraFlex and bring it into ArcGIS through the add-in can also use the Trimble Offline GNSS Corrections service for situations where real-time correction services are intermittent or unavailable. With this service, all data from the field is automatically processed in the cloud without user intervention, and the most accurate real-time or post-processed position is stored for each feature and made available for download through the Terra Office add-in for ArcGIS Pro.
Trimble Geospatial, geospatial.trimble.com
Data Capture App
A customizable mobile application for GIS data collection
1Capture is a mobile GIS editing application that is multi-use and configurable. It provides accurate and reliable data collection and editing in the field for a multitude of asset, job, and survey types. Customizable rules and actions work to improve data quality at the point of capture. This ensures that good quality data is captured at the source, minimizing re-surveys. The built-in rules engine automatically validates and corrects the GIS and non-GIS data collected, whether working online or offline. 1Capture connects with a variety of GIS environments, including Esri ArcGIS and open-source technologies such as PostGIS and Geoserver.
1Spatial, 1spatial.com/us/
AUTONOMOUS
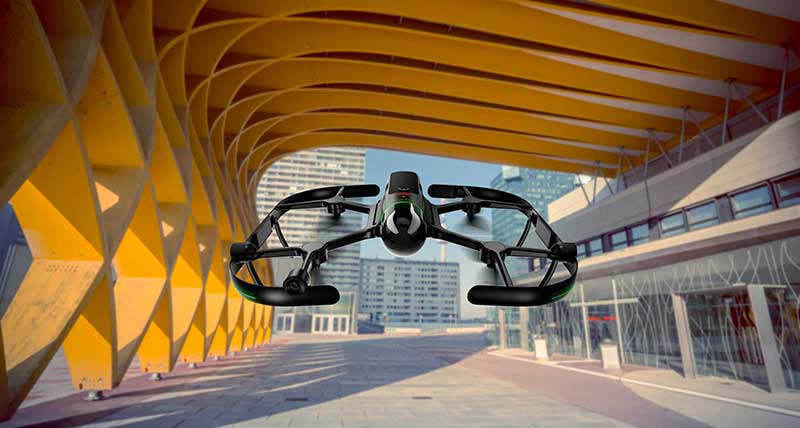
Heavy-Lift Delivery UAV
An off-the-shelf, ready-to-fly delivery aircraft for last mile delivery
The RDST Longtail features a RDS2 drone winch, enabling payloads to be deposited safely from altitude so that spinning rotors are kept far from people and property. The UAV can deliver or retrieve payloads up to 5 kg and over a distance of 11 km, making it suitable for various applications such as local parcel or food delivery, emergency medical deliveries, water sampling programs, offshore logistics, search and rescue operations and more. The UAV can also auto-release packages without the need for a recipient to be present at the delivery location. This is made possible by the all-new bag auto-release mechanism, allowing for easy pickups and auto-releasing of bags during deliveries. Designed to meet FAA regulations, the RDST Longtail is remote ID compliant with a factory-integrated remote ID beacon. The Premium edition of the drone can fly in inclement weather and features a quick-release battery system for minimal downtime.
A2Z Drone Delivery, a2zdronedelivery.com
GNSS INS
Suitable for multiple applications
The ANELLO GNSS inertial navigation system (INS) is designed for reliable long-term GPS-denied navigation and localization. Powered by optical gyroscope technology and artificial intelligence-based sensor fusion engine, the ANELLO GNSS INS delivers robust, high-accuracy positioning and orientation for applications such as agriculture, construction, trucking, and autonomous vehicles. It comes equipped with unaided heading drift of less than 0.5°/hr, dual multi-band real-time kinematic-capable GNSS engines, ASIL-D-ready automotive qualified CPU, automotive 2-wire Ethernet, and dual high-speed CAN FD interfaces. It also features dual RS-232 interfaces, hardware precision time protocol, IEEE 802.1AS. The ANELLO GNSS INS is IP68 waterproof, as well as resistant to dust, salt spray and chemicals.
ANELLO Photonics, anellophotonics.com
GPS-Guided Robot
Designed specifically for painting athletic fields
The Turf Tank Two features dual motor drives for enhanced torque and optimized wheels for traction. On its own and controlled through a tablet, the Turf Tank Two can paint a regulation soccer field for two teams of 11 players each in less than 24 minutes, a baseball or softball field in less than 11 minutes, a lacrosse field in less than 26 minutes, and a full 100-yard football field in less than 3.5 hours. It can also paint logos and numbers. The Turf Tank Two is 43 in x 33 in x 22.5 in. It weighs 123 lbs, without paint or the battery installed, and it can hold 5.5 gallons of paint. Enhanced features of the Turf Tank Two also include a revamped sprayer module and advanced control features — including a redesigned front panel that has convenient pause/resume options with LED indicators displaying the robot’s status and a start/stop sprayer button. An LED indicator also comes on the battery. Its batteries are rechargeable. Because of the robot’s precision and accuracy, it uses significantly less paint and eliminates the overspray that is common with either painting by hand or using many of the older paint machines and sprayers on the market. The GNSS-guided Turf Tank Two uses a base station to enhance its accuracy, while its onboard GNSS receiver acts as a rover.
Turf Tank, turftank.com
DEFENSE
Solar-Electric HAPS UAS
Provides an alternative to conventional sensing and communications systems
PHASA-35 is an ultra-light weight, solar-electric high altitude pseudo satellite (HAPS) unmanned aerial system (UAS) designed as an alternative to conventional systems such as satellites or conventionally powered aircraft for cost-effective imagery and communications. PHASA-35 uses photo-voltaic arrays to provide energy during the day, which is stored in rechargeable cells to maintain flight overnight. The UAS is designed to provide a persistent, stable platform for monitoring, surveillance, communications, and security applications. When connected to other solutions, it provides military and commercial customers with capabilities that are not currently available from existing air and space platforms. PHASA-35 can also be used to deliver communications networks including 5G, as well as provide other services, such as disaster relief and border protection. The UAS also has a flexible payload design that enables a large and varied range of sensor capabilities to be carried and updated. The PHASA-35 is suitable for military communications, military surveillance, commercial communications, maritime surveillance, border security, agricultural monitoring, and environmental monitoring.
BAE Systems, baesystems.com
GPS Receiver
A-PNT device featuring M-code GPS technology
NavGuide is a field-installable replacement to the defense advanced GPS receiver (DAGR), designed for quick integration into current DAGR mounts and accessories without mission interruption. NavGuide features a 3 in, full-color, graphical user interface for dismounted soldiers, and easily integrates with existing mounted platforms and systems. The device leverages the advanced M-code GPS signal with enhanced jamming and spoofing protection. NavGuide is portable, versatile, and precise, and enables vehicular, handheld, sensor, and gun laying applications that enable the military to defeat adversaries in a variety of challenging threat environments.
BAE Systems, baesystems.com
OEM
Vertical Location Device
For a variety of applications that rely on precise PNT
Pinnacle delivers precise, floor-level, vertical positioning for geolocation applications. It offers altitude measurements that meet the Federal Communications Commission mandate of 3 m accuracy. Pinnacle works with existing barometric pressure sensors in devices to improve quality and accuracy. Pinnacle technology provides z-axis data and has been demonstrated in independent testing to deliver 94% accuracy. Pinnacle data is derived from a proprietary network built for public safety, operated and maintained by NextNav, for wide availability. SDK, API, and Unity plug-in options make it easy to integrate 3D geolocation technology into existing applications.
The device also offers consistent vertical location abilities available throughout large urban areas. Pinnacle is available across the United States, is currently being deployed across Japan, and is being tested in France for local emergency repsonse agencies.
NextNav, nextnav.com
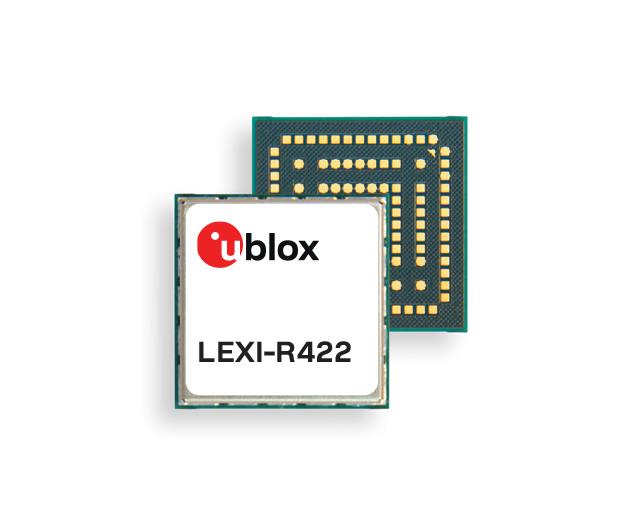
LTE-M/NB-IoT Module
For small asset trackers
The LEXI-R4 module is customized for size-constrained application requirements. The device is suitable for small asset trackers, such as pet and personal trackers, micro-mobility devices, and luggage tags. The LEXI-R4 module supports all LTE-M and NB-internet of things (IoT) bands, with an RF output power of 23 dBm. It is natively designed to support GNSS AT commands, and its dedicated port enables easy integration with any u-blox M10-based GNSS module, such as the MIA-M10. Additionally, the module can connect to additional positioning services, such as AssistNow and CellLocate. The compact size of the module, measuring 16 mm x 16 mm, results from a 40% footprint reduction in dimensions compared to the previous u-blox SARA-R4. Due to its small size, it leaves room for larger antennas, which can improve RF performance, or for larger batteries. Another feature of the LEXI-R4 is its 2G fallback capability. Whenever LTE-M/NB-IoT coverage conditions are not optimal, it continues to function by falling back onto a 2G network. The company said this feature could be helpful in countries where LTE-M/NB-IoT networks have yet to be fully deployed.
u-blox, u-blox.com































 Frank Van Diggelen, Google, and President of ION.
Frank Van Diggelen, Google, and President of ION. GPS World Editorial Advisory Board member, John Fischer, Safran Navigation and Timing, and Matteo Luccio at the Safran booth.
GPS World Editorial Advisory Board member, John Fischer, Safran Navigation and Timing, and Matteo Luccio at the Safran booth. Chuck Stoffer (left) and Jeffery Sanders (right), UHU Technologies.
Chuck Stoffer (left) and Jeffery Sanders (right), UHU Technologies.